Research on Drug Quality under the International General Technical Requirements of Haibu Pharmaceutical
Classification:
Haibu Growth Camp
Release time:
2020-12-16
2018年4月13日,北京海步医药科技股份有限公司喜迎美国三和药业 T3 PHARMA LINK创始人兼总裁汤丽雅博士、南京柏贤医药科技有限公司总经理肖柏明博士莅临指导,并围绕“药物质量法规ICH与分析方法”及“分析方法的起点,终点及周期管理”等药品质量研究方面开展了精彩的学术报告。

我公司坚持“以技术为核心、以人才为根本”的治企方针,在医药科研领域中不断强化提高研发人员的科研水平,此次学术报告也为公司的化学药物研发工作注入了先进的研发思路,并通过公司项目的案例分析深入浅出的将药物研发的理论与实践进行了完美的结合。
汤丽雅博士在此次培训中,针对药物质量法规ICH方面:对药物分析方法尤其是不同研发阶段的分析方法的规范及合理性做出指导;除药典标准、CFDA发布各药物研发指导原则外,针对各类杂质的控制方法及要求,如基因毒性杂质、异构/手性及残留溶剂等。分析方法的起点、终点及周期管理方面:包括分析方法的质量源于设计,方法的目标,风险评估;分析方法的验证、确认及转移等。经过此次系统的讲解培训,相信今后同事们分析方法开发过程中的思路将会更明晰。

汤博士很详细的对ICHQ8、Q9、Q10进行了讲解,对于药品研发,过去关注的是数据传递、可变的输出量,而现在更关注知识传递和基于科学/一致的输出量;质量风险管理,过去缺乏定义,非结构化,而现在使用结构化流程;Q10药品质量体系,提示我们在未来,应建立贯穿产品生命周期的质量体系,且整个生命周期质量体系要保持一致性;Q12指导企业,在操作规程中应增加超出规定限度之外的情况下,如何操作和处理,以减少上市后变更的复杂性,为我们的研发工作提供了新的思路。
关于基因毒性杂质,ICH M7有详细的基因毒性杂质分类,概况起来大致分为以下几种:
| Impurity Class 杂质类别 |
Definition 定义 |
Guidance for control 控制指导 |
| Class 1 |
Known mutagenic carcinogens 已知致突变致癌物 |
Control at or below compoundspecific acceptable limit 控制在化合物特异性的特接受限度以下 |
| Class 2 |
Known mutagens with unknown carcinogenic potential (bacterial mutagenicity positive*, no rodent carcinogenicity data) 致癌性未知的已知致突变物(细菌致突变性阳性*,无啮齿动物致癌性数据) |
Control at or below acceptable limits (appropriate TTC) 控制在可接受限度(合适的TTC)以下 |
| Class 3 |
Alerting structure, unrelated to the structure of the drug substance; no mutagenicity data 警示结构,与原料药结构无关;无致突变性数据 |
If non-mutagenic = Class 5 如无致突变性,归为5类 If mutagenic = Class 2 如有致突变性,归为2类 |
| Class 4 |
Alerting structure, same alert in drug substance or compounds related to the drug substance 警示结构,与原料药结构有关;无致突变性数据 |
Q3A Q3B
|
| Class 5 |
No structural alerts, or alerting structure with sufficient data to demonstrate lack of mutagenicity or carcinogenicity 无警示结构 |
基因毒性杂质分析中使用的分析技术,归类起来有以下几种:
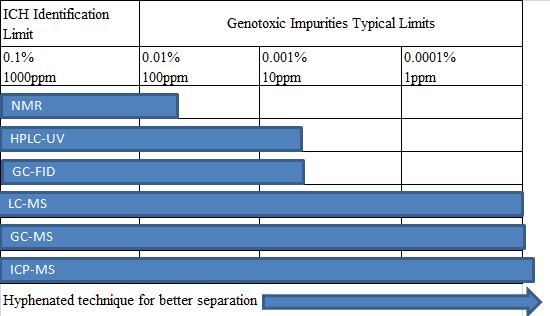
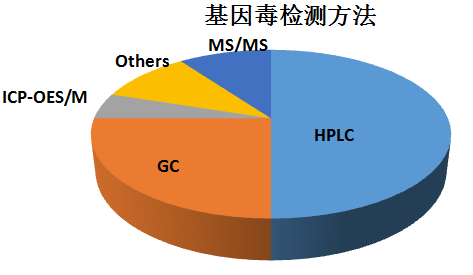
对于大多数药物的基因毒性杂质,可以用LC-MS及GC-MS来进行检测,各种分析技术方法的使用百分比见下表:
对于分析方法的质量源于设计,汤博士更是有一套自己有效的DOE方法,可以使用“鱼骨图”或表格形式,分别分析各参数的风险因子,根据风险级别的大小,确定分析方法设计空间。
| Risk for Low or High Assay/Impurity Results(含量/有关物质风险评估表) | |||||
| Risk Factor (Failure mode) | Severity high=3 medium=2 low=1 |
Probability high=3 medium=2 low=1 |
Detectability high=1 medium=2 low=3 |
Numerical Rating S×P×D |
CQA |
| Environment | |||||
| Room Temperature | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Room Humidity(regular samples) | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | |
| Room Humidity(hydroscopic samples) | 3 | 2 | 1 | 6 | Y |
| Material | |||||
| sample | |||||
| Solvent (more risk on impurity) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | Y |
| Water (more risk on impurity) | 2 | 2 | 2 | 8 | Y |
| Analyst | |||||
| Weighting | 3 | 2 | 2 | 12 | Y |
| Mixing | 3 | 2 | 2 | 12 | Y |
| Transferring | 3 | 2 | 2 | 12 | Y |
| Glassware | |||||
| Volumetric flask & Pipette | 3 | 2 | 1 | 6 | Y |
| Autosampler Vial (more risk on impurity) | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | Y |
| Bottle & Baker | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | |
The red represents high risk, yellow represents medium risk, and green represents low risk.
Based on the results of the risk assessment and validation, determine the plan for method transfer validation to make it more scientific and reasonable.
Dr. Xiaoboming provided deeper insights and supplements during the lecture, reinforcing understanding through examples from the project, allowing colleagues to gain a deeper understanding of chemical drug development work.
The lecture lasted about 9 hours. Through this training, colleagues at Haibu Pharmaceutical benefited greatly. The advanced R&D ideas brought by the teachers broadened everyone's research and development perspective. The two teachers also expressed their recognition of everyone's learning attitude and enthusiasm, believing that in future drug development work, they can apply what they have learned to contribute to the company's vigorous and stable development.
Next Page
Next Page






